类签名
/**
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea 又是这个大神
*/
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {}
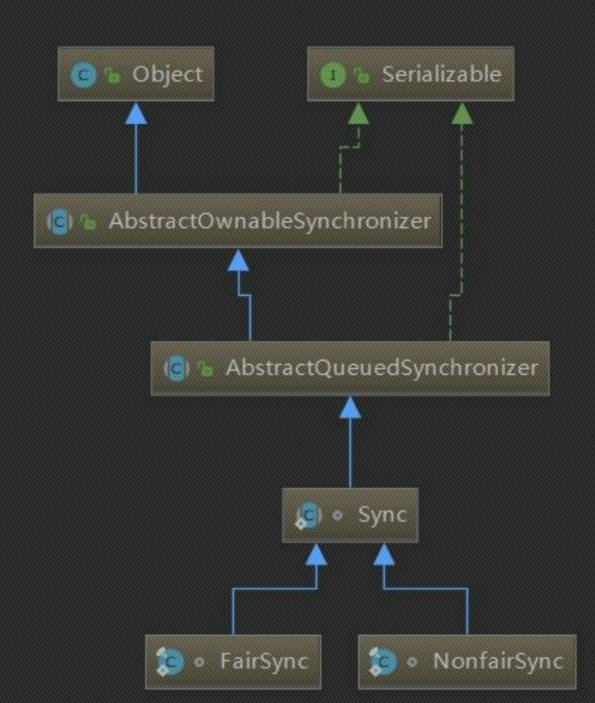
继承关系
源码分析
总览
Sync:是提供AQS实现的工具,类似于适配器,提供了抽象的lock(),便于快速创建非公平锁。FairSync(公平锁):线程获取锁的顺序和调用lock()的顺序一样,FIFO。NoFairSync(非公平锁):线程获取锁的顺序和调用lock()的顺序无关,抢到CPU的时间片即可调度。
构造方法
/**
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}.
* This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}.
*/
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync(); // 默认非公平锁
}
/**
* Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the
* given fairness policy.
*
* @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy
*/
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync(); // 可以指定使用公平锁
}
/**
* Acquires the lock.
*
* <p>Acquires the lock if it is not held by another thread and returns
* immediately, setting the lock hold count to one. 如果没有被另一个线程持有锁,会设置count持有数量为1 ,并立刻返回
*
* <p>If the current thread already holds the lock then the hold 如果当前线程已经持有锁,count会自增,并且立刻返回
* count is incremented by one and the method returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the lock is held by another thread then the 如果锁被另一个线程持有,当前线程将被禁用以进行线程调度,并进入休眠状态,直到获得锁为止。此时,锁的持有计数将设置为一。
* current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until the lock has been acquired,
* at which time the lock hold count is set to one.
*/
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
获取锁
加锁和释放锁,都是交给Sync来调度, 而这个Sync是AQS的子类,
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
//线程在请求lock并被阻塞时,如果被interrupt,则此线程会被唤醒并被要求处理
//当尝试获取锁失败后,就进行阻塞可中断的获取锁的过程。调用AQS.doAcquireInterruptibly()
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
//默认获取的是非公平锁,失败后不会阻塞
//直接返回true或false
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);
}
//在规定时间内获取锁,获取不到则返回false
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
释放锁
// 将当前线程持有锁数量减一
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
Sync
Sync继承自AQS,有一个抽象方法lock(), 具体地实现看子类
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { // 继承了aqs
/**
* Performs {@link Lock#lock}. The main reason for subclassing
* is to allow fast path for nonfair version.
*/
abstract void lock();
/**
* Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in
* subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method.
*/
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // 当前线程
int c = getState(); // 获取state 是volitale的
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // cas 期待原值是0,是0才能塞入
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 设置哪个线程有访问权限
return true; // 申请成功
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // 当前线程是有访问权限的,上一次的大哥又来了
int nextc = c + acquires; // 加上
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true; // 申请成功
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases; // 减去要释放的数量
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) // 如果当前线程没有权限,要硬闯释放,那肯定不可能
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) { // 枷锁释放光了,没有债务了
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); // 还当事人一个自由,单身了
}
setState(c); // 设置成减完的状态
return free; // ret
}
}
NonfairSync非公平锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { // 非公平锁
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) // cas
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); // 自旋成功则设置该线程占有
else
acquire(1); // 调用父类AQS的acquire() , acquire中调用的是子类重写的tryAcquire(),而不是父类的直接抛异常的tryAcquire
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); // 调用的129行的,nonfairTryAcquire 加非公平锁
}
}
FairSync公平锁
static final class FairSync extends Sync { // 公平锁
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1); //用于以独占模式获取锁,并通过调用至少一次 tryAcquire 方法来获取锁。如果获取锁失败,线程将被排队,并可能重复阻塞和解除阻塞,
}
/**
* Fair version of tryAcquire. Don't grant access unless
* recursive call or no waiters or is first.
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { // 公平锁
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // currentThread
int c = getState(); // 重入状态 hasQueuedPredecessors为false才继续cas,为true也就是有线程排队的话直接else if 了 ,尝试之前会利用 hasQueuedPredecessors() 方法来判断 AQS 的队列中中是否有其他线程,如果有则不会尝试获取锁(这是公平锁特有的情况)。
if (c == 0) { // 首先进入hasQueuedPredecessors方法中,判断当前队列是否有线程正在排队,当有线程正在排队时,代表锁还在被释放的过程中,仅仅只是锁的状态码被改变,但锁没有被释放,所以线程仍需入队排队
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && // 当进入hasQueuedPredecessors方法中,发现没有线程正在排队时,代表锁此时并没有被人持有,此时可以尝试CAS操作获取锁,当获取成功,tryAcquire方法返回true,线程继续执行
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // cas自旋
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 设置当前线程独占
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // 锁重入,当前线程有权限,再次进入
int nextc = c + acquires; // nextc自增
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc); // 设置state, state标识着重入锁的进行进度
return true;
}
return false; // 有线程在排队喽。
}
}



